In the previous blog, we discussed what immersive experiences will look like in the metaverse. In this article, we’ll explore two of the recent emerging technologies, cryptocurrency (crypto), and non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and how they will play a crucial role in the metaverse experience.
We’ll explore:
- Key terms and definitions related to this topic
- Owning assets in a digital world
- Who is building the metaverse and why?
- What opportunities will the metaverse offer to enterprises?
An Introduction to Key Metaverse-related Terms
While crypto, NFTs, and the metaverse have been popular topics over the last few years, they are still emerging technologies. Before going deeper into the topic, it’s important to have a basic understanding of these concepts.
In the first blog, we defined the metaverse as physical reality merging with the digital universe. It includes shared virtual 3D worlds that are interactive, immersive, and collaborative. However, as the metaverse stands, it is non-interoperable with different platforms supporting disconnected worlds. In other words, it’s highly siloed and decentralized, which has made it difficult for enterprises to navigate.
Cryptocurrency, called crypto for short, is a digital currency that’s secured by cryptography, using blockchain technologies that makes it nearly impossible to counterfeit or double-spend. Much like the metaverse, crypto is decentralized, operating on disparate networks of computers using blockchain technology. One of the key alluring factors that have drawn many to cryptocurrencies is that it’s not issued by a single central, governing authority.
Non-fungible tokens, or just called NFTs, are digital assets that represent real-world objects like art, music, in-game items, and videos. Being non-fungible means that they cannot be traded one for one with other goods and assets. For instance, if a person lends someone their car, they cannot return with a different car. But if they lend someone twenty dollars, they can pay that person back with a different twenty-dollar bill, or an amount of bills equaling twenty dollars.
Much like cryptocurrencies, NFTs are secured on blockchain technology (also called metaverse blockchain). The most common blockchain is Ethereum, but they do not have to be exclusively created on that blockchain. As such, it makes it almost impossible to counterfeit, guaranteeing and proving their uniqueness. However, origin authenticity can be in question which is why it’s imperative IP ownership is validated. Given the digital aspect of the metaverse, crypto and NFTs naturally play a key role in the space.
Owning assets in a digital world
The hot trend right now is creating NFT drops and collections. Enterprises across industries, from high-end retail companies like Gucci to well-known brands such as Coca Cola have created NFTs. Moreover, many companies are already looking at strategic ways to incorporate the metaverse as another marketing channel, leveraging NFTs which can be purchased with traditional fiat currency, crypto (sometimes called metaverse coins).
The attraction to the metaverse and integrated financial and collectible assets taps into to three key benefits:
- The collectible nature of NFTs, reaching a culture that’s long existed with physical collectibles
- Experiences that meet people where they are already gaming or hanging out with friends, families, colleagues, and fellow users
- The decentralized nature of everything, empowering people that had to rely on governing “middle-man” entities
These aspects have acted as driving factors to the rising popularity and adoption of the metaverse. But these are really after effects to the entire concept of why companies are investing and building the metaverse.
Who is building in the metaverse and why?
The metaverse is the natural progression where technology and our everyday experience finally begin to merge. Much of the things we do in the physical world often include a digital element these days, and we can expect that won’t change anytime soon.
Companies are already making huge investments in the metaverse, with Meta, formerly Facebook, making waves last year with their repositioning. But they aren’t alone. There are roughly six layers that make up the metaverse, each with their own slew of companies that are investing in making it a reality.
As mentioned before, the three benefits driving the attraction to the metaverse are really after effects. One of the reasons why the metaverse is being built boils down more closely to our third point which is decentralization.
Developers and smaller entities, such as content creators of all shapes and forms as well as businesses, have found a new way to level the playing field. That attractive nature has drawn people to the early metaverse platforms like Decentraland and other evolving gaming platforms pushing into the space like Epic Games. Naturally, companies and brands are going to follow because of the opportunity it presents.
What opportunities will the metaverse offer to enterprises?
The key opportunity for enterprises is connecting with their target audiences in an authentic, organic, and digitally immersive yet humanistic way. Companies have bought digital real estate with the purpose to build digital stores, offering NFTs and digital apparel based on real-world items. Others have completed planned and promotional events such as NFT drops and in-game events.
Here’s some of the unique things brands have done in the metaverse:

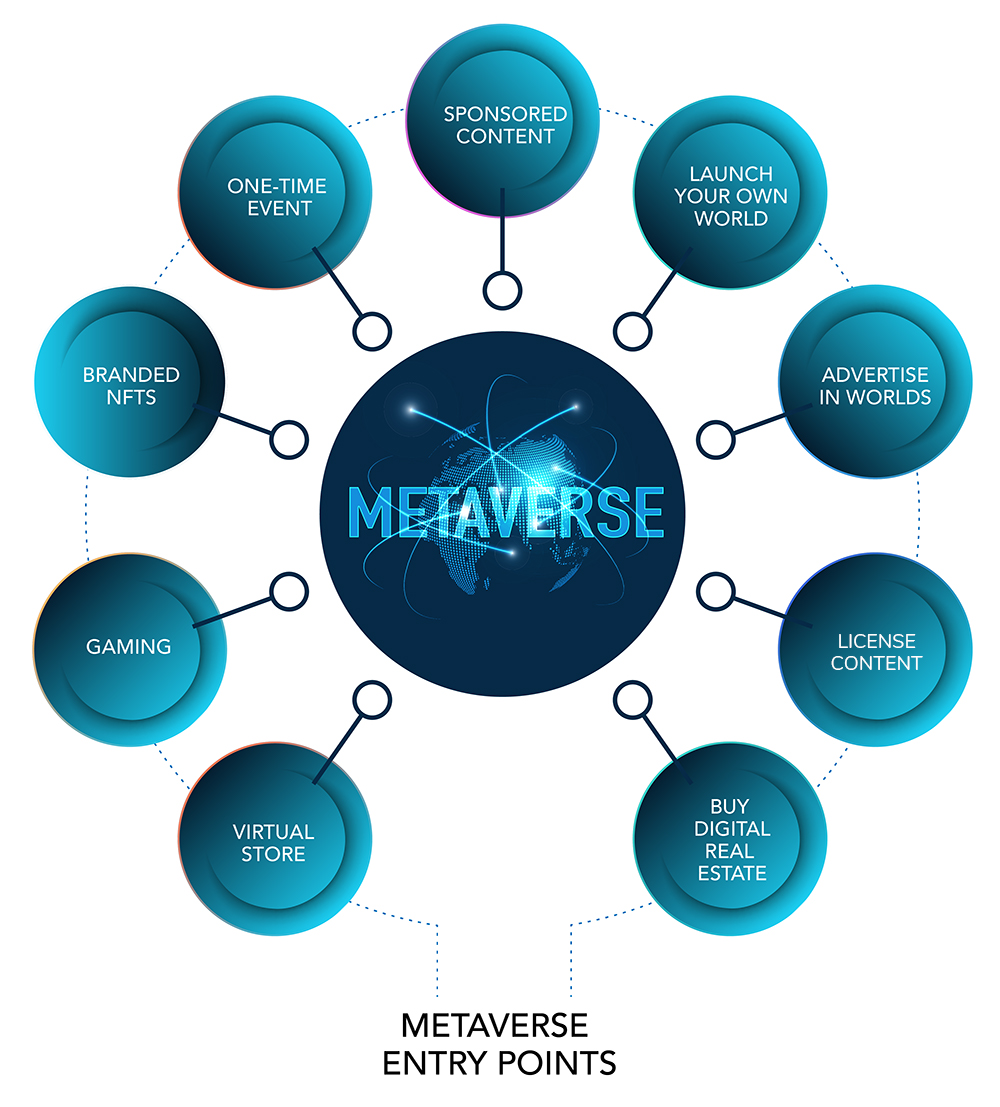
The challenge for many enterprises is simply expertise. Many do not have know-how both in their current skill set and technology stack to effectively start participating in the metaverse. Especially considering there are varying degrees of entry as well as different access points that all have their own outcomes and goals.
The common entry points we have seen include:
As we discussed in blog two of this series, artificial intelligence (AI) will play a key role in managing the underlying infrastructure of the metaverse and all the data it will generate. It will also play a critical role in creating digitally immersive experiences through synthetic content and 3D avatars to make the digital more lifelike—enabling the creation of virtual identities.
To help companies bridge the gap between where they are today and operating effectively in the metaverse, Veritone has launched a whole new offering to help support these new experiences. Veriverse, a suite of offerings that include synthetic voice, avatar, NFT, asset protection management solutions and services, aims to help companies not only enhance what they are doing today but make it easier to shorten their transition to web3. With our metaverse migration services, we’ll enable enterprises to assess their current capabilities, provide them a map to enter the metaverse, and make a successful entry.